關於我們

關於我們
About Us
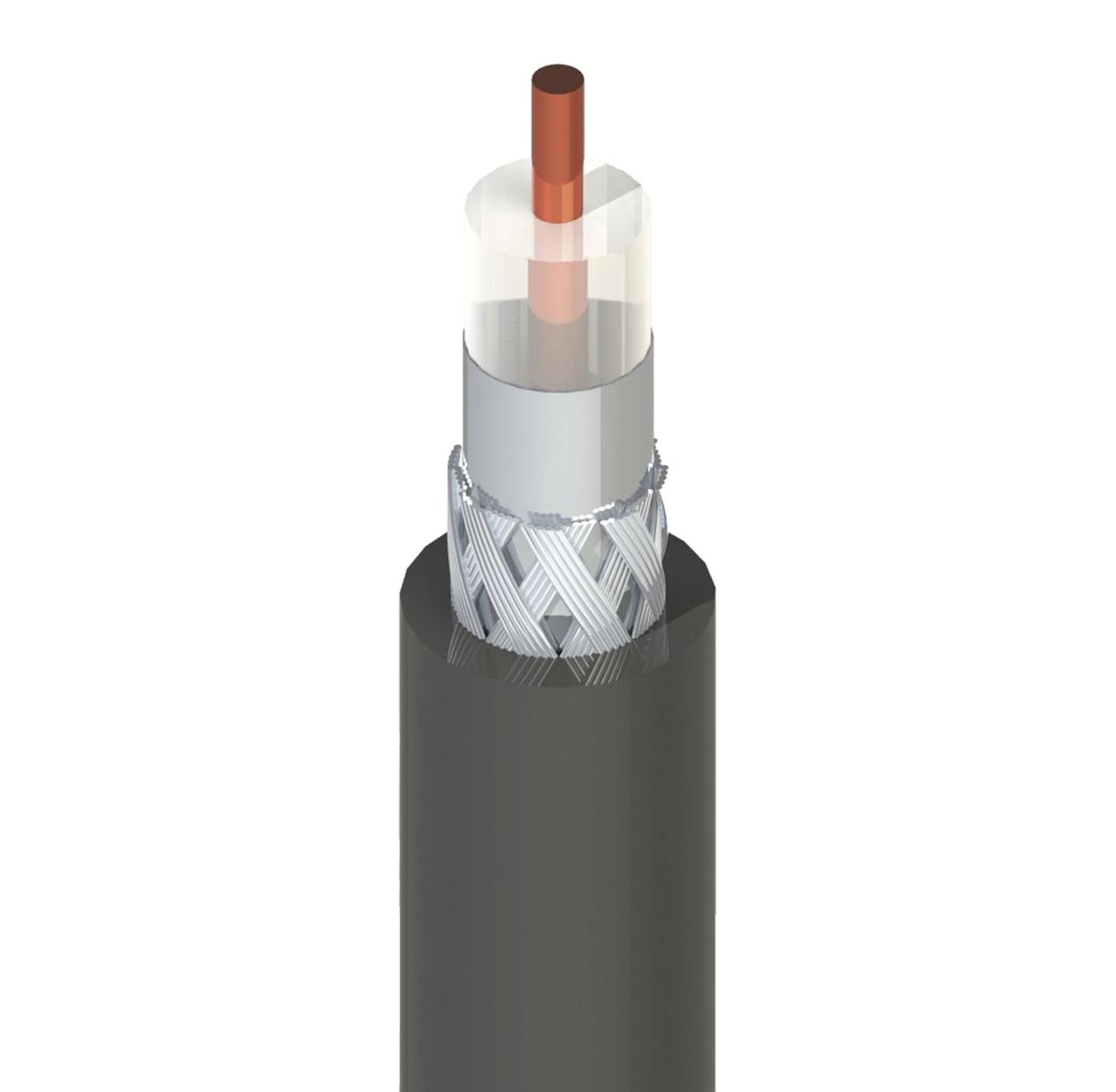
以低成本創造高品質之產品
良泉工業有鑑於科技的日新月異,傳統工業將面臨第二次工業革命,本公司為維繫產業生存,於2000年05月完成物理發泡線種之研發。
除了維持現有訂單運作外,將營運重心朝向特殊專業線材開發及內部管理體制之改善,以期再造良泉產業生存,以臻國際市場領域。
除了維持現有訂單運作外,將營運重心朝向特殊專業線材開發及內部管理體制之改善,以期再造良泉產業生存,以臻國際市場領域。

產品分類
Product Category